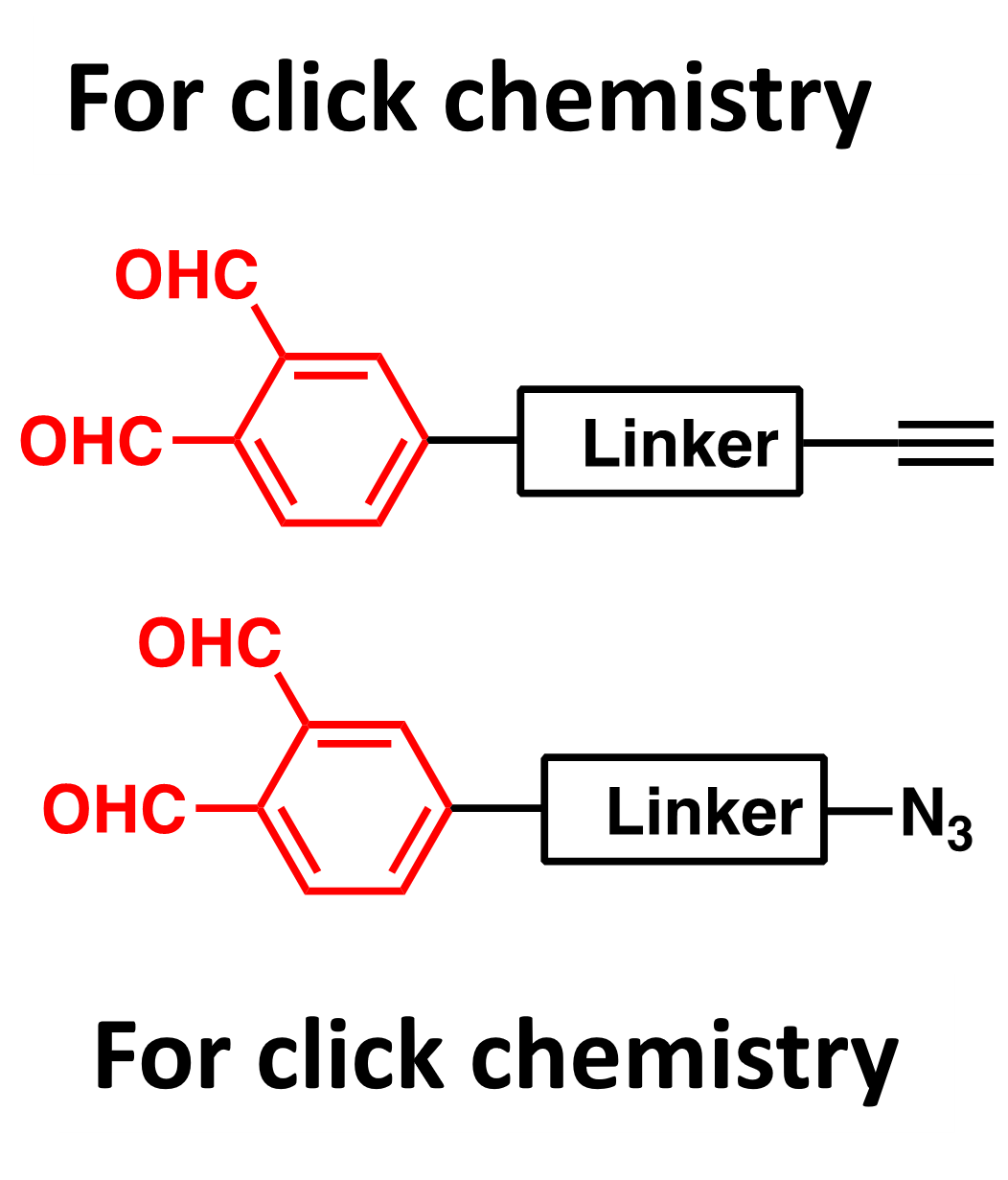
OPA-alkyne/azide: an efficient and versatile adapter
Click chemistry is a highly selective and very mild reaction. It is widely used in ADC drugs, biomarkers, and conjugation. OPA-azide/alkyne (including BCN/DBCO) serves as an efficient and versatile adapter that can directly modify antibodies. The modified antibodies have excellent water solubility and can be purified and then conjugated with a variety of commercial reagents, or they can be used directly in the next step without purification, enabling low-cost and high-throughput construction of antibody-drug libraries. The reagents can also be pre-conjugated with matching commercial reagents in a one-step synthesis to produce OPA-functionalized reagents.
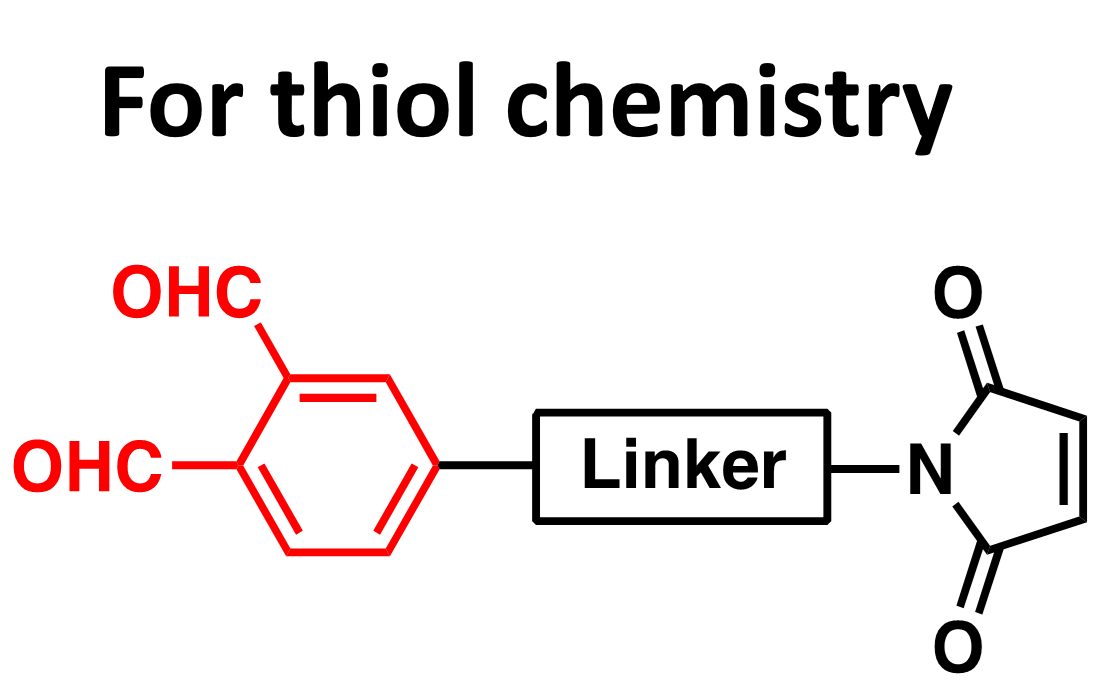
OPA Maleimide: A Highly Practical Antibody Conjugation Drug Reagent Kit.
OPA Maleimide allows for the coupling of any cytotoxin with a thiol (thio) group, such as DM1, to form a highly stable OPA toxin linker. This linker can be purified and stored long-term without degradation. The OPA linker can also be used immediately without purification. Its OPA component can modify large antibody molecules targeted at cancer cell surface receptors (such as Anti Her2 antibodies), endowing them with potent cancer cell-killing capabilities, essentially creating antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Moreover, the OPA reagent kit can be highly customized to possess different lengths, rigidities, and functionalities for antibody-drug conjugation agents. By assembling different toxins, antibodies, and linkers, OPA reagents can help quickly build libraries of antibody-drug conjugates for screening, supporting the development of new anti-cancer drugs.

OPA-chelator: stable and water-soluble conjugation reagents
Radioactive Drug Conjugates (RDCs) are one of the most promising directions in nuclear medicine targeted therapy. Their theranostic advantage gives them a significant advantage in the treatment and evaluation process. However, the reaction conditions for loading radionuclides in RDCs are relatively harsh, and their stability has been a major concern and challenge. OPA, as a reacting head, forms a highly stable five-membered cyclic amide structure with amines, compared to the traditional maleimide. Currently, this linker has shown excellent stability, good water solubility, and controllable Drug-to-Antibody Ratio (DAR) in the conjugation experiments with antibodies, nanobodies, and peptides.

OPA-Toxin: efficient and stable ADC conjugation reagent
ADCs (Antibody-Drug Conjugates) and PDCs (Peptide-Drug Conjugates) have become a highly important treatment modality in cancer therapy. It has been demonstrated that OPAs are highly compatible with a variety of toxins, such as MMAE, MMAF, Dxd, DM1, and others. Multiple linkers, including traditional linkers and cleavable linkers, have been validated as effective connectors between OPAs and toxins. Through the efficient conjugation of OPA-toxins and antibodies under mild conditions, water-soluble ADCs with the desired Drug-Antibody Ratio (DAR) have been obtained. To enable high-throughput screening of various toxins, OPA-linker- chloride and OPA-linker-PNP (p-nitrophenyl carbonate) can undergo direct chemical reactions with multiple toxins, thereby avoiding the need for complex synthetic routes to generate OPA-toxin conjugates. These OPA-toxin conjugates can be stably stored for years and can be conveniently prepared as stock solution for long-term use.

OPA-PEG: PEG modification reagent
Although a peptide or protein molecule demonstrates great efficacy in vitro, this biomolecule is quickly cleared from the body before it can be effective when tested in animal models or clinical trials, resulting in less-than-ideal therapeutic effects. By directly using our OPA-PEG reagent kit for PEGylation, it is theoretically possible to increase the effective concentration of the target peptide or protein in the body, reduce renal filtration, blood degradation, and immune rejection, thereby enhancing its pharmacokinetics and potentially achieving better clinical outcomes.
